Using Spring Boot Admin with Spring Cloud Kubernetes Discovery on OpenShift
Spring Boot Admin describes several ways of connecting clients to the admin server. If your Spring Boot applications are running on kubernetes or openshift then Spring Boot Admin can use the Spring Cloud Kubernetes discovery client. In this blogpost i’ll show you how.
Initial Setup
Setting up the Spring Boot Admin server is fairly easy. You only need one class annotated with @EnableAdminServer
and @SpringBootApplication and you’re good to go.
To use the Spring Cloud Kubernetes Discovery Client, we’ll add the spring-cloud-starter-kubernetes-discovery dependency.
Setting up dependencies
Here is an example build.gradle:
buildscript {
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
classpath "org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-gradle-plugin:2.2.2.RELEASE"
}
}
plugins {
id 'java'
}
apply plugin: "io.spring.dependency-management"
apply plugin: 'org.springframework.boot'
group 'nl.jcore.blog'
version '1.0-SNAPSHOT'
sourceCompatibility = 1.8
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
implementation 'de.codecentric:spring-boot-admin-server'
implementation 'de.codecentric:spring-boot-admin-server-cloud'
implementation 'de.codecentric:spring-boot-admin-server-ui'
implementation 'org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-starter-kubernetes'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-autoconfigure'
}
dependencyManagement {
imports {
mavenBom 'org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-dependencies:Hoxton.RELEASE'
mavenBom 'de.codecentric:spring-boot-admin-dependencies:2.2.2'
}
}
One important thing to note here is the extra spring-boot-admin-server-cloud dependency. All the other examples i found
didn’t mention needing this, but without this dependency the discovery of clients won’t work.
|
Setting up the main class
Next we’ll add two more annotations to our main class:
import de.codecentric.boot.admin.server.config.EnableAdminServer;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling;
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@EnableScheduling
@EnableAdminServer
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootAdminServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootAdminServerApplication.class, args);
}
}The EnableDiscoveryClient is from Spring Cloud to enable scraping the kubernetes API. The EnableScheduling annotation
is needed because this scraping is done with a scheduled job.
Internal connection details
The spring-boot-admin-server-cloud dependency adds a InstanceDiscoveryListener to your classpath, this class
listens
to
HeartbeatEvents from
the org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.event package.
The KubernetesCatalogWatch from the org.springframework.cloud.kubernetes.discovery package on his turn emits these HeartBeat events:
@Scheduled(
fixedDelayString = "${spring.cloud.kubernetes.discovery.catalogServicesWatchDelay:30000}")
public void catalogServicesWatch() {
try {
List<String> previousState = this.catalogEndpointsState.get();
// not all pods participate in the service discovery. only those that have
// endpoints.
List<Endpoints> endpoints = this.kubernetesClient.endpoints().list()
.getItems();
List<String> endpointsPodNames = endpoints.stream().map(Endpoints::getSubsets)
.filter(Objects::nonNull).flatMap(Collection::stream)
.map(EndpointSubset::getAddresses).filter(Objects::nonNull)
.flatMap(Collection::stream).map(EndpointAddress::getTargetRef)
.filter(Objects::nonNull).map(ObjectReference::getName) // pod name
// unique in
// namespace
.sorted(String::compareTo).collect(Collectors.toList());
this.catalogEndpointsState.set(endpointsPodNames);
if (!endpointsPodNames.equals(previousState)) {
logger.trace("Received endpoints update from kubernetesClient: {}",
endpointsPodNames);
this.publisher.publishEvent(new HeartbeatEvent(this, endpointsPodNames));
}
}
catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Error watching Kubernetes Services", e);
}
}The above method is annotated with @Scheduled, that’s why the @EnableScheduling is needed on our main class.
Configuration
You might run more than just spring boot applications in your OpenShift namespace, so we need to define a filter
for which services to scrape. This can be done with the property spring.cloud.kubernetes.discovery.service-labels,
a map is required here for label name and value.
Here is an example application.yml
spring:
application:
name: spring-boot-admin
boot:
admin:
ui:
brand: "JCore"
title: "JCore Boot Admin"
cloud:
kubernetes:
catalog-services-watch:
enabled: true
catalogServicesWatchDelay: 5000
discovery:
service-labels:
type: actuator
server:
port: 8080
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "*"
server:
port: 8081
logging:
level:
org.springframework.cloud.kubernetes: TRACE
de.codecentric.boot.admin.discovery.ApplicationDiscoveryListener: DEBUGNote that i’ve adjusted the logging level to receive more information on the discovery of clients. And i’ve set the management server port to a different value than the server port, so that our internal actuator information won’t be available from the route we’re going to define.
Deployment
The deployment consists of several objects:
-
DeploymentConfig
-
Service
-
Route
-
ServiceAccount
-
Role
-
RoleBinding
Authorization
To authorize our deployed container to scrape the kubernetes API and receive information about pods, services and endpoints we need to create a ServiceAccount and RoleBind it to a custom defined role.
Here is the example definition:
- kind: ServiceAccount
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: spring-boot-admin-sa
labels:
app: spring-boot-admin
- kind: Role
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: spring-boot-admin-role
labels:
app: spring-boot-admin
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
- endpoints
- services
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: authorization.openshift.io/v1
metadata:
name: spring-boot-admin-role-binding
namespace: ${PROJECTNAME}
labels:
app: spring-boot-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: spring-boot-admin-sa
namespace: ${PROJECTNAME}
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: spring-boot-admin-role
namespace: ${PROJECTNAME}| without authorization the admin server will log: io.fabric8.kubernetes.client.KubernetesClientException: Failure executing: GET at: https://demo/api/v1/namespaces/demo/endpoints . Message: Forbidden!Configured service account doesn’t have access. Service account may have been revoked. endpoints is forbidden: User "system:serviceaccount:demo:default" cannot list endpoints in the namespace "demo": no RBAC policy matched. |
Exposing the ports
Our application has two ports, one for the web interface and a management port for the actuator information. Because we’ll define a route for the web interface we need to split the services so that our actuator information isn’t obtainable through the route.
Here are the example definitions:
- apiVersion: route.openshift.io/v1
kind: Route
metadata:
labels:
app: spring-boot-admin
name: spring-boot-admin
spec:
port:
targetPort: 8080-tcp
to:
kind: Service
name: spring-boot-admin-webservice
weight: 100
- kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: spring-boot-admin-webservice
labels:
app: spring-boot-admin
spec:
ports:
- name: 8080-tcp
protocol: TCP
port: 8080
targetPort: 8080
selector:
app: spring-boot-admin
- kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: spring-boot-admin-actuator
labels:
app: spring-boot-admin
type: actuator
spec:
ports:
- name: 8081-tcp
protocol: TCP
port: 8081
targetPort: 8081
selector:
app: spring-boot-admin
The actuator service has an extra label defined: type: actuator. This is the same label from our application.yml: spring.cloud
.kubernetes.discovery.service-labels
|
DeploymentConfiguration
Last but not least our deployment configuration:
- apiVersion: apps.openshift.io/v1
kind: DeploymentConfig
metadata:
labels:
app: spring-boot-admin
name: spring-boot-admin
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
app: spring-boot-admin
deploymentconfig: spring-boot-admin
strategy:
activeDeadlineSeconds: 21600
recreateParams:
timeoutSeconds: 600
resources: {}
type: Recreate
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: spring-boot-admin
deploymentconfig: spring-boot-admin
spec:
serviceAccountName: spring-boot-admin-sa # <- Using our defined service account
containers:
name: spring-boot-admin
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
protocol: TCP
- containerPort: 8081 # <- exposing the management port
protocol: TCP
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
triggers:
- imageChangeParams:
automatic: true
containerNames:
- spring-boot-admin
from:
kind: ImageStreamTag
name: jcore-spring-boot-admin:latest
namespace: demo
type: ImageChange
- type: ConfigChangeResult
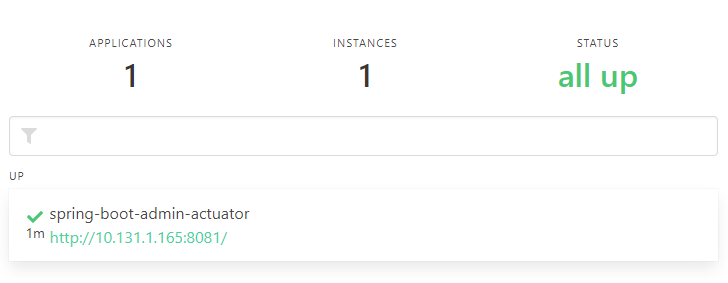
If all went well the Spring Boot Admin should show its spring-boot-admin-actuator service connection, and the application will log scheduled updates from Spring Clouds KubernetesCatalogWatch:
- - - -
[ scheduling-1] o.s.c.k.d.KubernetesCatalogWatch : Received endpoints update from kubernetesClient: [spring-boot-admin-1-w6k2t]
- - - -